Shoulder Replacement
If You Need Any Help Contact With Us
+91 98713 30000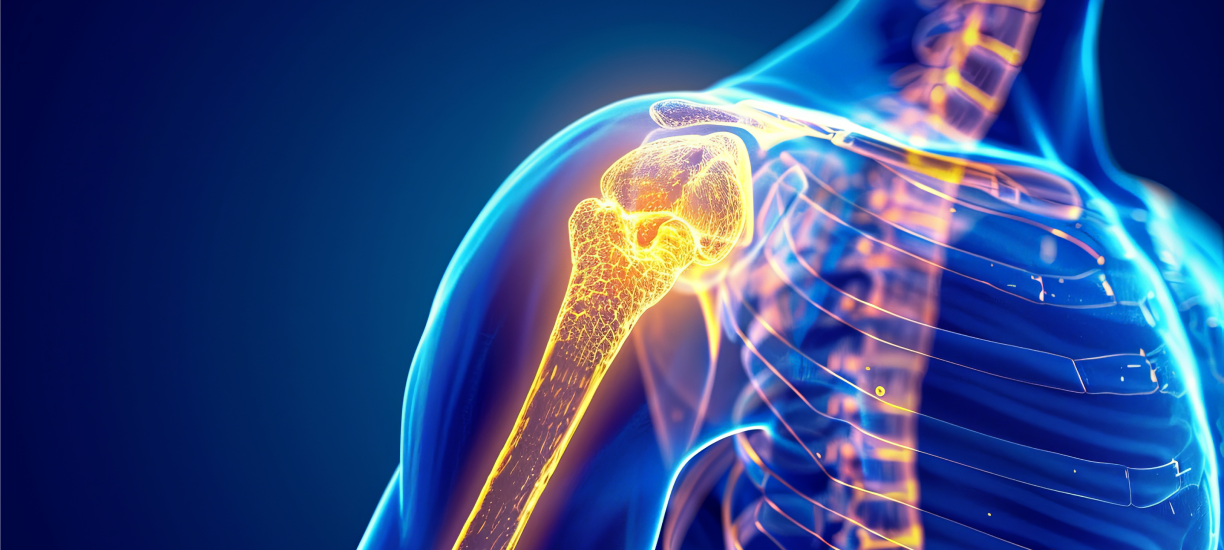
Shoulder Replacement
Understanding Shoulder Arthritis and the Need for Replacement
Shoulder pain and stiffness can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. One of the leading causes is osteoarthritis, commonly known as wear-and-tear arthritis. This condition leads to the gradual degeneration of the cartilage within the shoulder joint, exposing bare bone and causing discomfort. Other types of arthritis, including inflammatory arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, and rotator cuff tear arthritis, can also contribute to severe joint deterioration.
The shoulder comprises two primary joints:
- The glenohumeral joint (where the upper arm bone meets the shoulder blade)
- The acromioclavicular joint (between the collarbone and the shoulder blade)
As arthritis progresses, symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion become more pronounced. Some individuals may experience fluctuations in symptoms, influenced by factors like weather changes or activity levels.
When is Shoulder Replacement Recommended?
Shoulder replacement surgery is a highly effective solution for patients whose pain persists despite non-surgical treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. If shoulder pain interferes with routine activities, persists even at rest, or results in severe mobility loss, an orthopedic evaluation may be necessary.
Anatomy of the Shoulder Joint
The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body and consists of three key bones:
- Humerus (upper arm bone)
- Scapula (shoulder blade)
- Clavicle (collarbone)
It is a ball-and-socket joint where the head of the humerus fits into the glenoid cavity of the scapula, allowing for extensive movement. When arthritis or injury damages these structures, replacement surgery becomes a viable option.
Shoulder Replacement Surgery – The Procedure
In shoulder replacement, the damaged portions of the shoulder are replaced with artificial components (prostheses). The procedure may involve:
- Total Shoulder Replacement – Both the ball (humeral head) and socket (glenoid) are replaced.
- Stemmed Hemiarthroplasty – Only the humeral head is replaced.
- Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement – The ball and socket positions are switched for better function when rotator cuff tendons are damaged.
Common Causes Leading to Shoulder Replacement
- Osteoarthritis – Age-related joint degeneration
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – Autoimmune inflammation
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis – Resulting from injuries or fractures
- Rotator Cuff Tear Arthritis – Due to chronic rotator cuff damage
- Avascular Necrosis – Bone death due to disrupted blood supply
- Severe Fractures – Especially in osteoporotic individuals
Preparing for Surgery
- Choose an experienced orthopedic surgeon.
- Undergo pre-operative medical evaluations, including X-rays, MRI, and blood tests.
- Maintain optimal health with controlled blood pressure and diabetes.
- Discontinue certain medications, such as blood thinners, if advised.
- Arrange for post-surgery assistance at home.
Surgical Procedure and Implants
The surgery, which typically lasts about two hours, involves the removal of damaged bone and cartilage, followed by the implantation of:
- Cemented Prosthesis – Fixed using surgical cement.
- Uncemented Prosthesis – Designed to allow natural bone growth for fixation.
- Reverse Shoulder Replacement – Used in cases of severe rotator cuff dysfunction.
Each prosthetic component is designed for durability and mimics natural joint movement, ensuring long-term relief and improved mobility.
Post-Surgical Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Hospital Stay– Typically 1-3 days post-surgery
- Pain Management – Medications including NSAIDs and opioids for short-term relief
- Physical Therapy – Begins soon after surgery to restore strength and flexibility
- Home Recovery – Arm support with a sling for 2-4 weeks, gradual increase in activities
Recovery Tips for Better Outcomes
- Follow prescribed home exercises to enhance mobility.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects or sudden arm movements.
- Keep the surgical site clean and dry.
- Seek assistance when needed for daily tasks.
- Avoid driving for 2-4 weeks post-surgery.
Expected Results
Many patients experience significant pain relief and improved range of motion following shoulder replacement. With proper rehabilitation, they can return to an active lifestyle with minimal discomfort. If you’re considering shoulder replacement surgery, consult with Dr. Rajeev K. Sharma for expert guidance and personalized care.
